Pet Anatomy
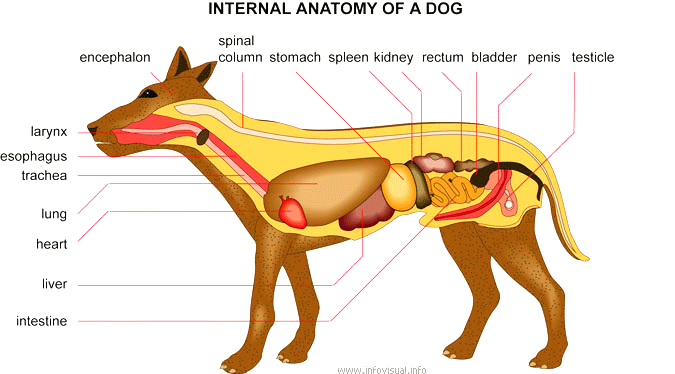
Carnivorous domestic mammal raised to perform various tasks for
humans.
- Encephalon: Seat of the intellectual capacities of a cat
- Lung: Respiratory organ
- Spinal column: Important part of the nervous system
- Stomach: Part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the small intestine
- Spleen: Hematopoiesis organ that produces lymphocytes
- Kidney: Blood-purifying organ
- Rectum: Last part of the intestine
- Bladder: Pocket in which urine collects before it is eliminated
- Penis: Copulative male sexual organ
- Testicle: Sperm producing sexual organ
- Intestine: Last part of the digestive tract
- Liver: Bile-producing digestive gland
- Heart: Blood-pumping organ
- Lung: Respiratory organ
- Trachea: Tube that carries air to the lungs
- Esophagus: First part of the digestive tract
- Larynx: Part of a dog's throat that contains the vocal cords
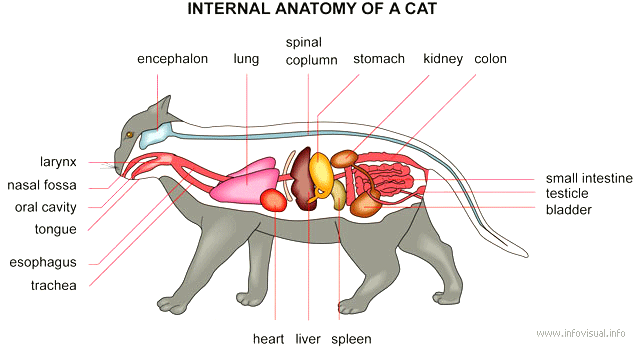
Carnivorous mammal of the feline family, with retractile claws. There are both wild and domestic varieties.
- Encephalon: Seat of the intellectual capacities of a cat
- Lung: Respiratory organ
- Spinal column: Important part of the nervous system
- Stomach: Part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the small intestine
- Kidney: Blood-purifying organ
- Colon: Large intestine
- Small intestine: Last part of the digestive tract
- Testicle: Sperm producing sexual organ
- Bladder: Pocket in which urine collects before it is eliminated
- Spleen: Hematopoiesis organ that produces lymphocytes
- Liver: Bile-producing digestive gland
- Heart: Organ that pumps blood
- Trachea: Tube carrying the air to the lung
- Esophagus: First part of the digestive tract
- Tongue: Taste organ of a cat
- Oral cavity: Chamber of the mouth
- Nasil cavity: Chamber of the nose
- Larynx: Part of a cat's throat that contains the vocal cords
Information courtesy of Animal World USA.



 ShareThis
ShareThis